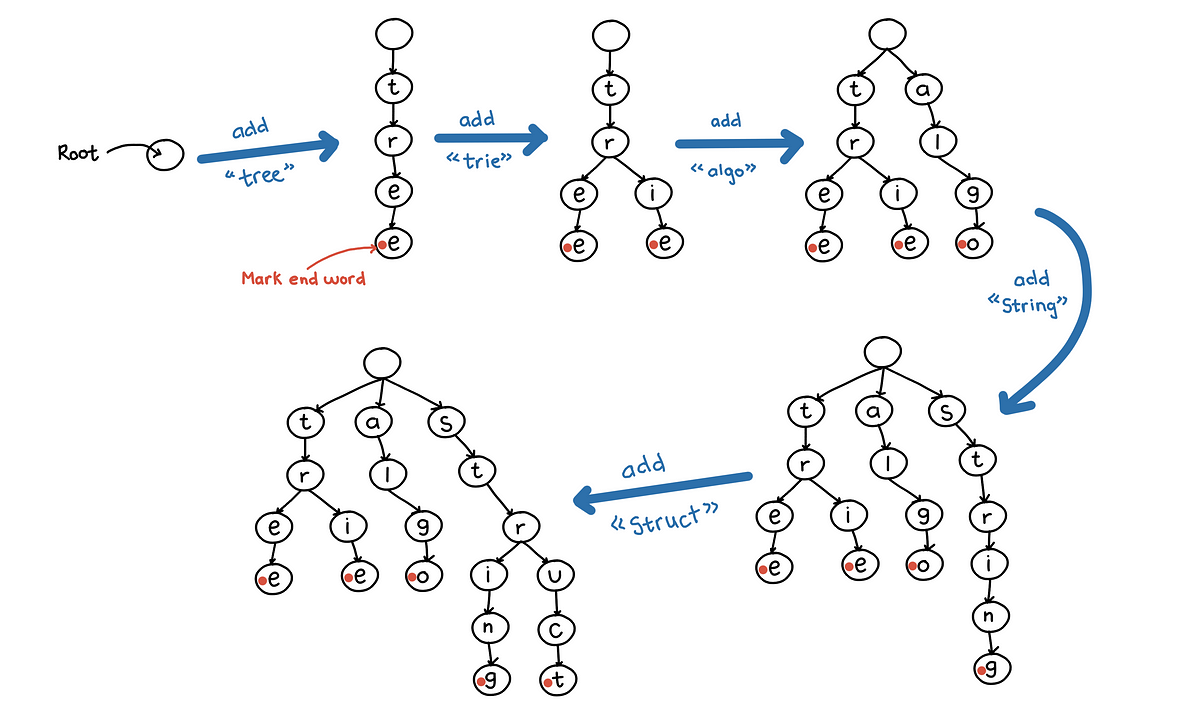
Trie Data Structure
- A Trie (pronounced as "try") is a tree-like data structure that stores a dynamic set of strings, usually used to solve problems related to words and prefixes. It is also known as a prefix tree because it can efficiently handle queries related to prefixes.
- Key Characteristics
- Efficiency: Tries provide efficient insertion, deletion, and search operations, generally proportional to the length of the word (O(m), where m is the length of the word).
- Prefix Searching: Tries are particularly useful for prefix-based searches, as all strings with a common prefix share the same initial path in the tree.
- Video explanation
- Leetcode question
class Node:
def __init__(self):
self.children = {}
self.end = False
class Trie:
def __init__(self):
self.root = Node()
def insert(self, word: str) -> None:
curr = self.root
for w in word:
if w not in curr.children:
curr.children[w] = Node()
curr = curr.children[w]
curr.end = True
def search(self, word: str) -> bool:
curr = self.root
for w in word:
if w not in curr.children:
return False
curr = curr.children[w]
return curr.end
def startsWith(self, prefix: str) -> bool:
curr = self.root
for w in prefix:
if w not in curr.children:
return False
curr = curr.children[w]
return True